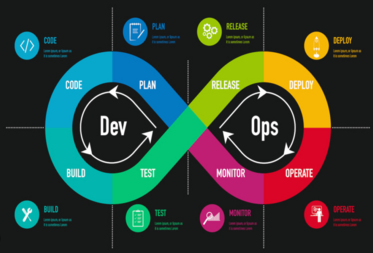
DevOps is a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to improve collaboration, communication, and efficiency throughout the software development lifecycle. It aims to automate and streamline the process of building, testing, deploying, and managing software applications, leading to faster delivery of high-quality software.
Key principles of DevOps include:
- Continuous Integration (CI): The practice of integrating code changes frequently into a shared repository, often several times a day. This ensures that new code changes are tested and validated continuously, reducing the risk of integration issues.
- Continuous Delivery (CD): The practice of automating the process of deploying software changes to production or other environments in a rapid and reliable manner. Continuous delivery enables teams to release software updates to users quickly and efficiently.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): The practice of managing and provisioning infrastructure resources (such as servers, networks, and storage) through code and automation tools. Infrastructure as Code allows for the automated creation and configuration of infrastructure, leading to consistency, scalability, and repeatability.
- Automation: DevOps emphasizes the automation of manual and repetitive tasks throughout the software development lifecycle, including building, testing, deployment, and monitoring. Automation reduces errors, accelerates processes, and frees up time for more strategic tasks.
- Collaboration and Communication: DevOps promotes collaboration and communication between development, operations, and other stakeholders involved in the software delivery process. Teams work together closely to align goals, share knowledge, and address challenges effectively.
- Monitoring and Feedback: DevOps emphasizes the importance of monitoring software applications and infrastructure in real-time to detect issues, identify bottlenecks, and gather feedback. Monitoring allows teams to continuously improve the performance, reliability, and user experience of their software products.
- Culture and Mindset: DevOps is not just about tools and technologies; it's also about fostering a culture of continuous improvement, experimentation, and learning within organizations. DevOps encourages teams to embrace change, take ownership of their work, and focus on delivering value to customers.
DevOps practices are supported by a wide range of tools and technologies, including version control systems (e.g., Git), continuous integration servers (e.g., Jenkins, CircleCI), configuration management tools (e.g., Ansible, Puppet, Chef), containerization platforms (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes), and monitoring solutions (e.g., Prometheus, Grafana).





Leave a comment